- Introduction
- Particle Network – Overview
- Chain Abstraction – Unlocked
- Universal Accounts
- Universal Liquidity
- Universal Gas
- Particle Network L1: Key Features
- Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS)
- BTC Connect
- The Team
- Conclusion
Introduction
The world of Web3 has embraced the continuous genesis of new on-chain infrastructure projects.New frontiers of user-experience are pushing into the crypto-mainstream, borne on the back of the prevailing crypto bull-run. However, user adoption of Web-3 products and services has grown at a notably slow rate, especially relative to Web-2 apps and services. There is an undercurrent that is actually making it tougher for new-comers, as well as a prominent chunk of the prevailing casual users from venturing further into the blockchain universe.
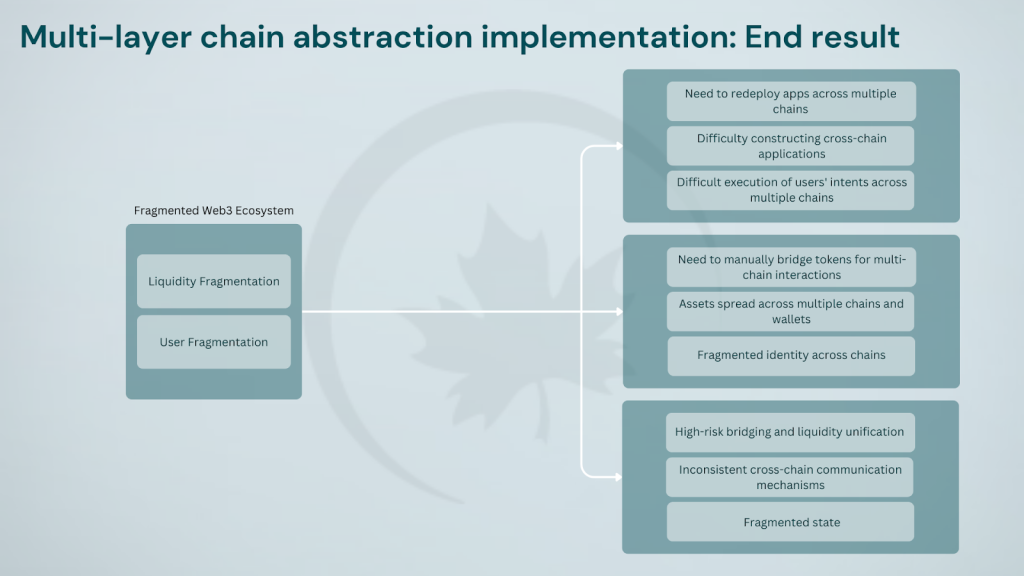
At the heart of this issue lies a series of small but significant obstacles. Each public blockchain and its associated dApps come with their own set of unique requirements. This fragmentation creates a complex ecosystem that can be overwhelming for many users. Users’ accounts and assets are split across different chains, making it costly and difficult for them to move across the ecosystem and leverage different dApps. Users must juggle multiple wallets, manage different tokens, and navigate disparate interfaces. This fragmentation can quickly erode the initial excitement of exploring a new platform or feature.
For nascent dApps, this situation poses a considerable threat. Many of these applications aim to offer cutting-edge experiences but struggle to overcome the inherent friction in the ecosystem. The challenge is twofold: providing an exceptional user experience while also addressing the broader usability issues of the blockchain space. The recurring theme among all breakout products worldwide is that they provided a better user experience relative to any incumbents or competitors they went up against.
In this context, simplifying the overall user experience across various blockchain services means addressing a critical need. In order for decentralized applications to achieve similar success, the onchain user experience must be as seamless and convenient as possible. These breakthroughs are aligned with a defining cause in the Web3 space: enhancing accessibility and usability. By streamlining interactions across different chains and dApps, these platforms are paving the way for greater participation. Any platform that serves the purpose of practically simplifying the overall user experience not only facilitates wider blockchain adoption but also delivers on a key measure of business success: customer satisfaction.
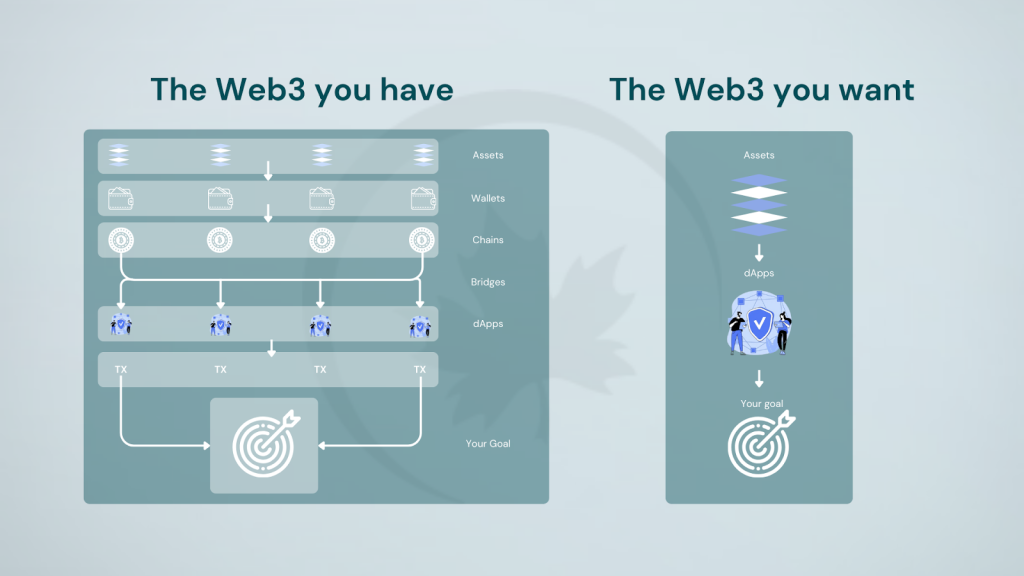
Furthermore, users must now manage independent accounts across different chains. They must also hold native tokens to pay for gas and facilitate transactions of all kinds. This further compounds the issue. A single asset like USDT, distributed across chains, cannot be centrally used in an automated, one-click manner. For example, a Tron-based USDT holder cannot immediately use that USDT on the Ethereum network, even though they have the token. Assets are locked to specific chains, limiting their utility. As the number of chains grows, the need for cross-chain interactions increases. But the user’s ultimate concern is nothing related to the super-sophisticated backend, seed phrases and bridging mechanisms.
We need a decentralized world where anyone can do anything on any blockchain without needing to go through cumbersome onboarding and bridging processes. This creates a steep learning curve, as bridging between chain types requires specific knowledge. Consequently, it introduces additional labor and cognitive load for end-users as they navigate the ecosystem. This ‘need’ is actually a ‘barrier-to-entry’ into various crypto-ecosystems. The ‘cognitive load’ is the marginal mental resistance added with each extra platform or chain in the user’s sphere. That, more than anything, negatively affects net user experience, especially when it becomes increasingly difficult over time to have the same level of autonomy and ease-of-access in the same ecosystem. Hinged on the collaborative properties of chain abstraction, Particle Network is the forefront state-of-the-art platform to break this ceiling.
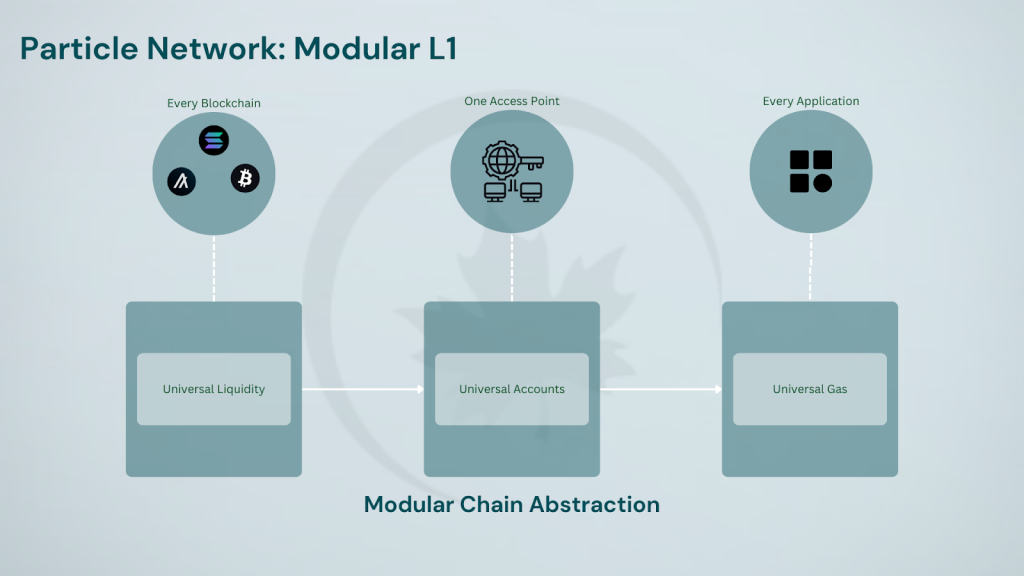
The core idea behind Chain Abstraction is pretty straightforward – blockchain technology should be invisible to users. In other words, users should be able to execute logic from one point of execution, eliminating the need for users to switch networks, sign transactions on different chains, or manage independent balances across networks. For the first time, users can seamlessly interact with a dApp from any supported chain, using any token, all without ever leaving the UI. To enable this, the network focuses on three critical functionalities: Universal Liquidity, Universal Accounts and Universal Gas.
Particle Network – Overview
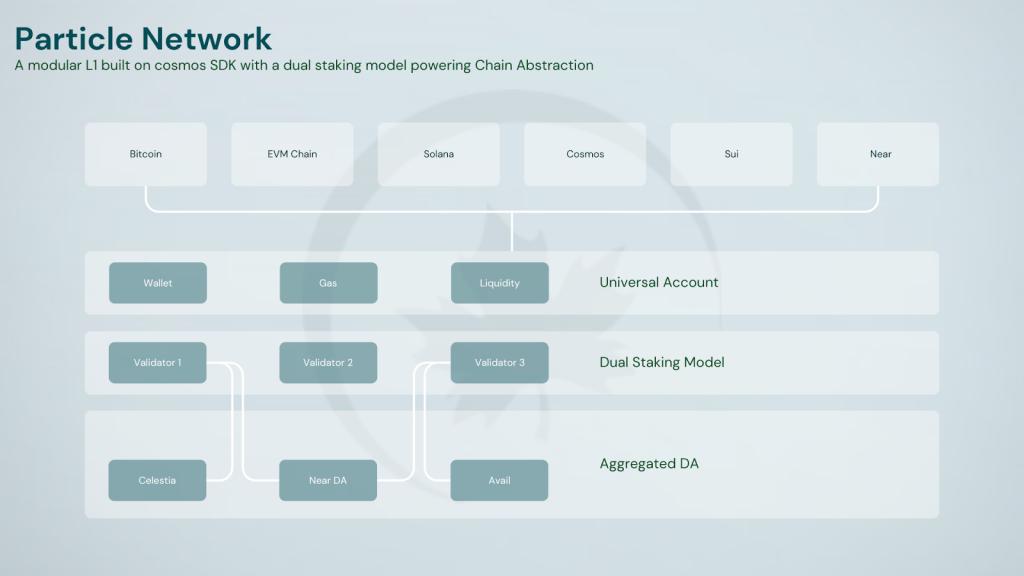
Particle Network is a Layer-1 blockchain built with the Cosmos SDK, equipped with a high-performance EVM execution environment.
Particle Network’s modular L1 blockchain powers chain abstraction and Universal Accounts spanning multiple chains, abstracting away wallets, gas, and unifying liquidity. It acts as a universal settlement layer, empowering existing L1s, L2s, and non-EVM blockchains through account coordination. The Particle Network L1 addresses the above issues through three core functional modules and an innovative chain design. It allows users to create a Universal Account spanning all public blockchains, providing them with a unified address and liquidity/balance across them. This facilitates seamless cross-chain transactions, effortlessly consolidating the liquidity from different chains for transactions anywhere, also enabling users to pay for gas fees with any token, on any chain.
Particle’s three core functional modules are the Master Keystore Hub, the Decentralized Messaging Network, and the Decentralized Bundler Network, which are covered in the ‘Chain Abstraction: Unlocked’ section. The Particle L1 is one component of Particle’s broader chain abstraction stack, which consists of Universal Accounts providing a simple interface for unifying token balances across different chains, Universal Liquidity enabling UAs on the backend, and Universal Gas allowing users to pay gas fees in any token they hold.
Summarizing the plethora of seamless upgrades that Particle Network brings us, we get chain abstraction infrastructure that enhances interoperability for chains, for both dApps, and end-users, unlike the traditional solutions that target specific audiences such as AMBs (which exist primarily as low-level developer-centric primitives). This approach elevates blockchain interoperability and accelerates the industry’s shift from fragmentation to unification. Particle Network enables chains to share a single user base and liquidity through Universal Liquidity, allows dApp developers to deploy their applications once to serve users across the entire ecosystem, and provides end-users with Universal Accounts for seamless multi-chain and cross-chain transactions. Particle Network also offers a multitude of API endpoints designed to facilitate high-speed, flexible blockchain interactions.
Chain Abstraction – Unlocked

The primary goal of chain abstraction is to streamline the fragmented modular landscape of Web3, particularly focusing on enhancing the user experience. Most of this fragmentation can be attributed to how hard manually interacting with multiple chains is. Users not only need to manage their balances on every chain, but also bridge assets across, hold multiple gas tokens, etc. Chain abstraction simplifies this largely. Chain abstraction requires the ecosystem as a whole to embrace it at different levels to build interconnected systems supporting it.
An on-chain account is ultimately the bridge between a user and the blockchain, storing balances on-chain and defining all activities and interactions with any blockchain-native program. And Particle Network does indeed address the above issues at the fundamental level, in a multi-faceted, account-centric method.
Historically, users have relied on bridges for filling their multi-chain needs, which have been subjects of multiple hacks, leading to Billions in stolen user funds and often create a flurry of confusion amongst users. Hence they’ve proven over time to be a great source of risk and insecurity. Account-level chain abstraction represents a critical evolution in blockchain technology, that addresses the need for seamless communication without this massive exposure in terms of security and the user’s valued assets, happening right within the user’s main interaction point –their account. Unlike traditional bridges, which have often been sources of risk and insecurity, chain abstraction builds upon account and execution abstraction while introducing new infrastructure at the network layer.
This approach eliminates the complexities of cross-chain interactions, culminating in a unified goal: enabling users to perform on-chain actions without needing to know which specific blockchain they’re using. In the current crypto landscape, users face the challenge of managing liquidity across multiple L1s and L2s, often settling for suboptimal user experiences due to fragmented on-chain liquidity sources and the need to understand complex technical nuances. Chain abstraction aims to simplify this experience by abstracting away these intricacies from the average user. By doing so, it removes the need for users to be aware of the underlying blockchain technology or the multitude of L1s and L2s involved, potentially paving the way for mass adoption. This breakthrough in user experience could be the missing link in onboarding the next generation of businesses and users to blockchain and crypto-native ecosystems, offering a seamless interface where the complexities of blockchain technology fade into the background.In a chain-abstracted ecosystem, the user experience is dramatically simplified. Users interact with decentralized applications (dApps) by simply connecting their wallet, signing the intended operation, and waiting for settlement. The intricate processes of acquiring necessary assets on the target chain and finalizing the settlement are handled behind the scenes.
The infrastructure required to implement chain abstraction at a broad, Web3-wide scale, is represented by frameworks like CAKE. The CAKE framework consists of three key layers: the permission layer, the solver layer, and the settlement layer. The Permission layer incorporates elements like Account Abstraction, Intents, Policies, and Key Management, effectively managing user authorization. The Solver layer handles the complex computations and routing necessary for cross-chain operations. The Settlement layer, which includes technologies such as oracles, bridges, pre-confirmations, and other back-end features, works to ensure secure and efficient execution of transactions. The Settlement layer is particularly crucial for solvers and sophisticated actors, as well as user-facing applications. Its components collaborate to help solvers manage risk and provide enhanced execution for users. This layer also encompasses important aspects like data availability and execution proofs, which are essential for creating a secure environment for application developers. These features ultimately translate into robust security guarantees for end-users, fostering a safer and more reliable blockchain ecosystem. By abstracting these complex processes, the CAKE framework aims to make blockchain interactions as seamless and user-friendly as possible, potentially paving the way for broader adoption of blockchain technology.
Universal Accounts
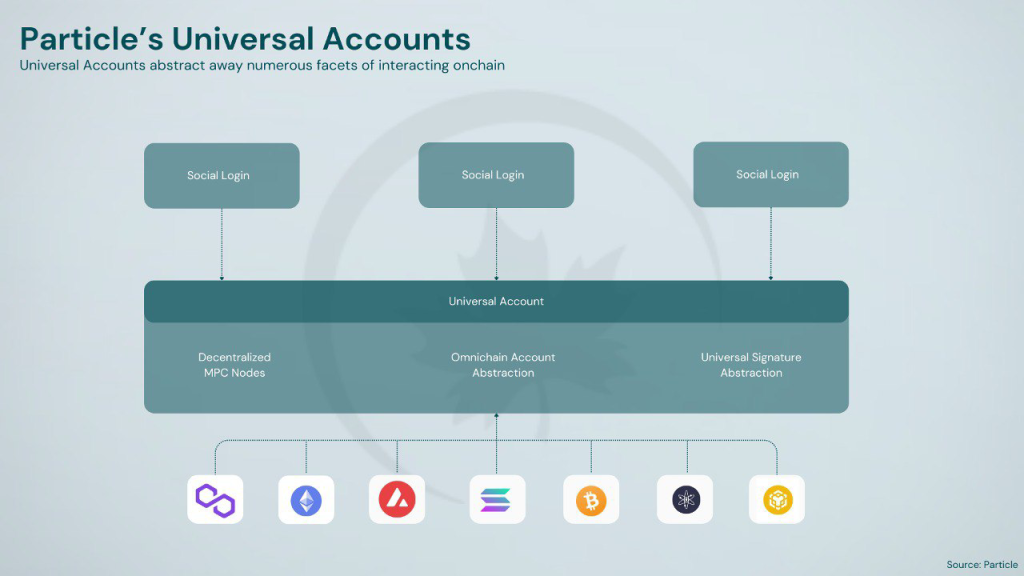
Universal Accounts are a key feature enabling Particle Network to achieve chain abstraction. These accounts give users a single address, balance, and interaction point across the multi-chain ecosystem. The foundation of Universal Accounts lies in the aforementioned Omnichain Smart Contract Wallet. At their core, UAs are ERC-4337 smart accounts attached to a pre-existing EOA (externally owned address), unifying token balances across multiple chains by automatically routing and executing atomic cross-chain transactions. With a Universal Account, users maintain a single balance and address across all chains. By tapping into Universal Liquidity (see below), users can perform cross-chain transactions automatically, resulting in a unified and seamless user experience. Moreover, Particle Network’s Universal Accounts function as Smart Accounts, which can bundle multiple UserOperations into a single transaction. This approach streamlines complex, multi-step transactions, saving users time and resources compared to solutions like NEAR, which process signatures linearly for such operations, requiring users to initiate a new transaction at every step.
The foundational technology of Particle’s Universal Accounts is the Omnichain Smart Contract Wallet. By separating code logic from state storage, Particle Network ensures that any modification to a user’s Universal Account is immediately and synchronously updated across all chains.The submitted UserOperations trigger the execution of the underlying transactions on external chains—L1s, L2s, and L3s, such as Polygon or Base—through Bundler Nodes. The interdependencies of the UserOperations are coordinated by Particle’s Modular Nodes to ensure they are executed correctly, with the final execution status consolidated and settled on the Particle Network L1. This interface is built on top of existing wallets and leverages Particle’s liquidity layer-Universal Liquidity- to execute atomic cross-chain transactions and route funds from a user’s balance across different chains as needed.
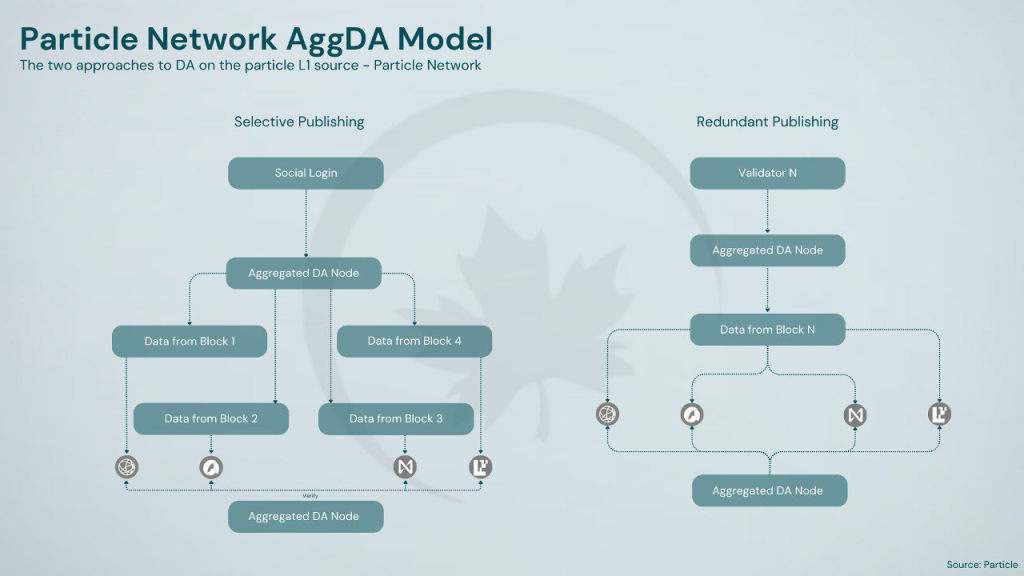
Unlike competitors like NEAR and Polygon’s AggLayer, which require users or developers to migrate to their platforms or opt into specific frameworks, Particle Network’s solution does not impose migration costs on existing users or developers. Particle Network’s Relayer Nodes can monitor the execution status of UserOperations events without the need for dedicated asset bridges or Arbitrary Message Bridges (AMBs). This approach ensures compatibility with existing infrastructure while maintaining a streamlined and efficient system.
To complete complex multi-step transactions, users only need to authorize them once, saving time and costs on complex transactions, and the layer-agnostic Universality enables it to encompass almost all public chains. Furthermore, unlike traditional blockchains that rely on a single data availability provider, Particle Network aggregates multiple sources, including Avail, Celestia, and NEAR DA. This aggregation enhances the robustness and redundancy of data availability, ensuring higher security and reliability for the blockchain.
Universal Liquidity
Universal Liquidity refers to the layer of the Particle Network responsible for the automatic execution of transactions submitted via UAs. Particle Network’s Universal Liquidity architecture leverages a modular node setup and a Decentralized Messaging Network (DMN) to ensure automatic operations across all chains. Liquidity abstraction unifies liquidity across a wide range of blockchains via the optimistic execution of cross-chain atomic transactions and swaps, allowing users to interact with a plethora of networks without holding tokens on a specific chain. This system facilitates seamless cross-chain interactions, unifying balances across Universal Accounts and automating the movement of funds between chains by drawing liquidity from the user’s balances when needed.
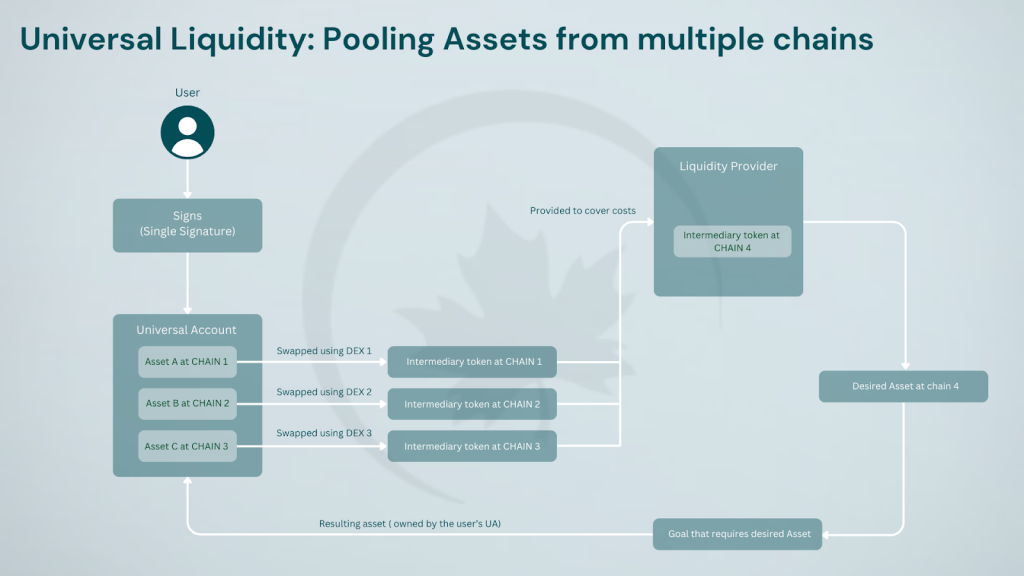
Universal Liquidity is facilitated through an atomic swap mechanism involving Liquidity Providers (LPs). Users can seamlessly utilize their assets distributed across multiple chains by exchanging them for an intermediary token (e.g. USDC) with the LPs. The LPs then transport this intermediary token across the relevant chains, releasing it on the target chain where it can be exchanged for the desired asset using a decentralized exchange (DEX). This approach eliminates the need for manual bridging and allows transactions using any token, all coordinated and settled through Particle Network. Users experience cross-chain interactions as if they were on a single chain. When a user joins an app that uses Particle Network’s Universal SDK, their EOA (e.g. MetaMask, Keplr) signs into a Universal Account, enabling funding and usage across different chains without bridging, all powered by Universal Liquidity.
Universal Gas
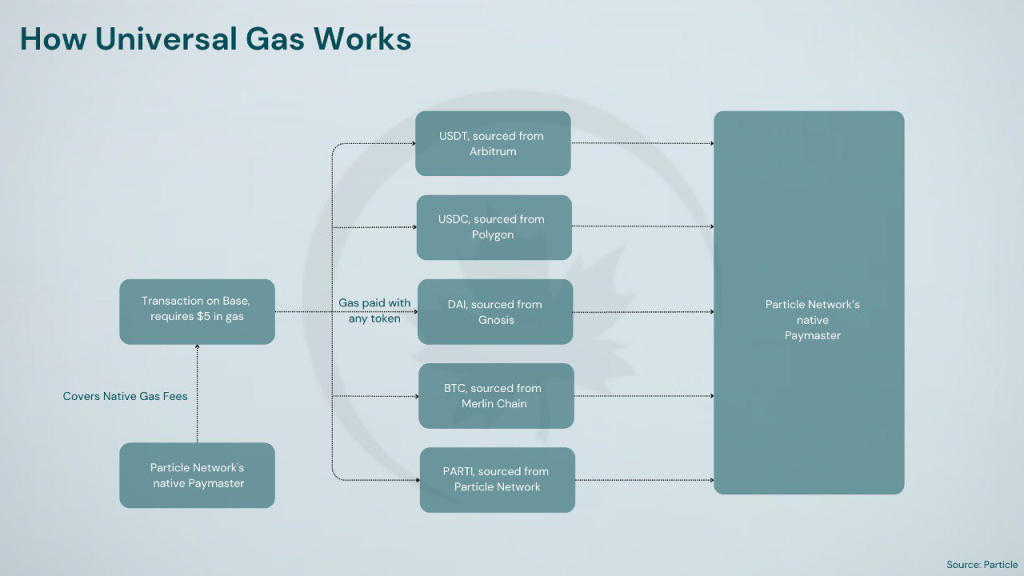
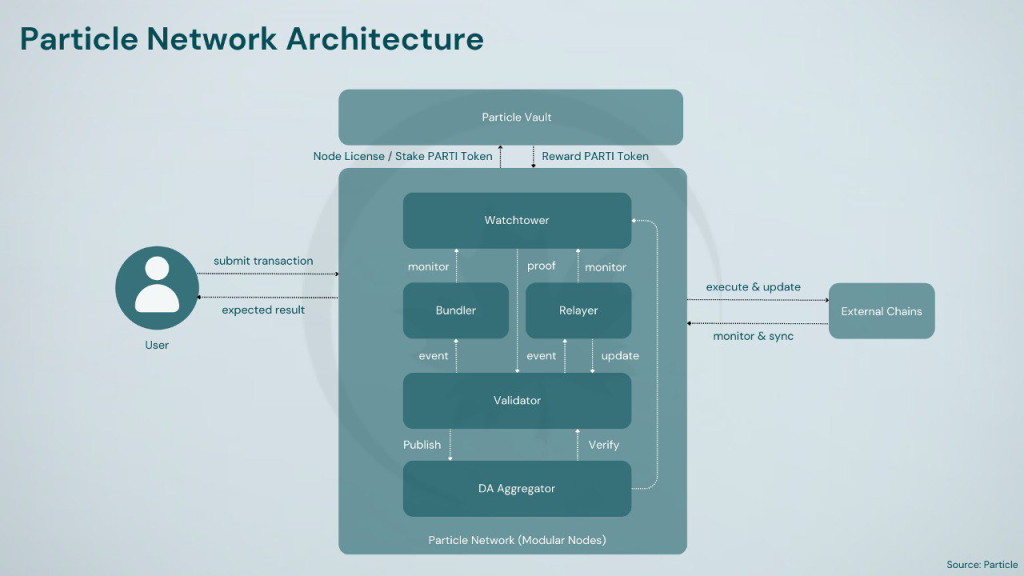
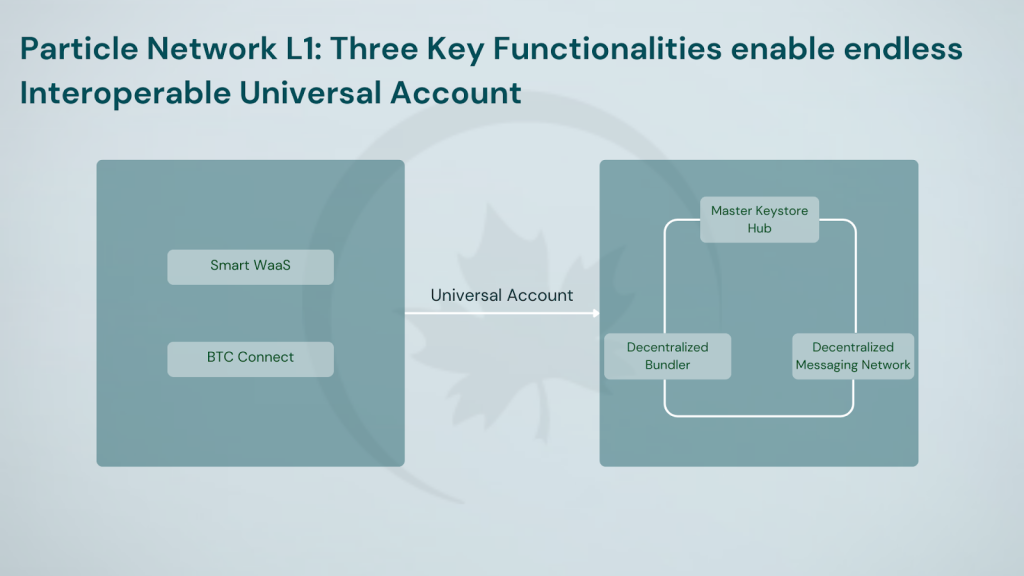
Universal Gas is implemented through an Omnichain Paymaster, enabling users to pay for gas fees across different chains using any token of their choice, removing the need for multiple tokens such as SOL, ETH, or MATIC. Particle Network’s Omnichain Paymaster initially settles gas fees in the native $PARTI token on the Particle Network L1. Users can then pay the Paymaster in their preferred token for the equivalent value consumed within their UserOperations, effectively utilizing any token as gas across the entire ecosystem. To establish a universal coordination layer, Particle Network introduces a lightweight infrastructure that outsources DA while utilizing a novel consensus mechanism, based on three core modules: Master Keystore Hub (MKH), Decentralized Messaging Network, Bundler Nodes. Particle Network employs the Decentralized Bundler to initiate UserOperations on external chains, the Decentralized Messaging Network of Relayer Nodes to monitor and settle the execution status, and the Master Keystore Hub to ensure consistent state management across chains.
Particle Network L1: Key Features
The Particle L1 represents an innovative approach to blockchain architecture, combining high-performance capabilities with robust security measures. At its core, it employs an EVM-compatible execution environment, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of existing Ethereum-based applications and tools.
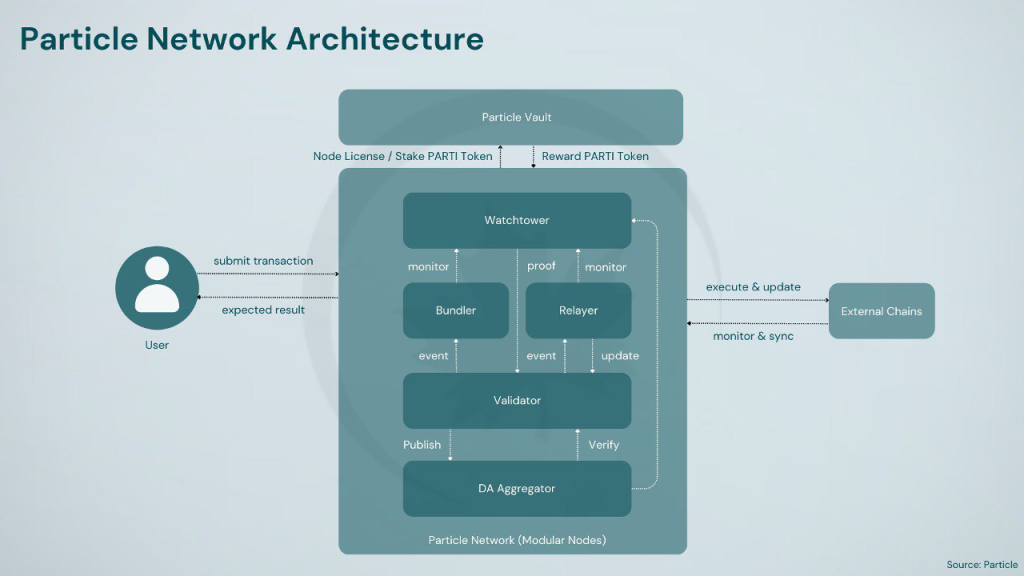
The network’s security is underpinned by a unique dual-token staking model, leveraging both Bitcoin (BTC) and its native PARTI token. This hybrid approach aims to provide enhanced stability and security to the network. A key feature of Particle L1 is its reliance on a distributed network of specialized nodes, known as Modular Nodes, for consensus and data availability. This modular design allows for broad participation in network operations, with nodes categorized based on their specific functions. Bundler nodes handle the execution of cross-chain UserOps, facilitating seamless interactions across different blockchain networks. Relayer nodes are tasked with monitoring transaction statuses and communicating this information back to the Particle L1 for settlement, ensuring transparency and reliability in transaction processing. Watchtower nodes play a crucial oversight role, monitoring the performance of other nodes in the bundler and relayer networks, as well as providing essential execution and fraud proofs for each block within an epoch. This comprehensive node structure aims to create a decentralized, efficient, and secure blockchain ecosystem capable of handling complex cross-chain operations while maintaining high performance and reliability.
Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS)
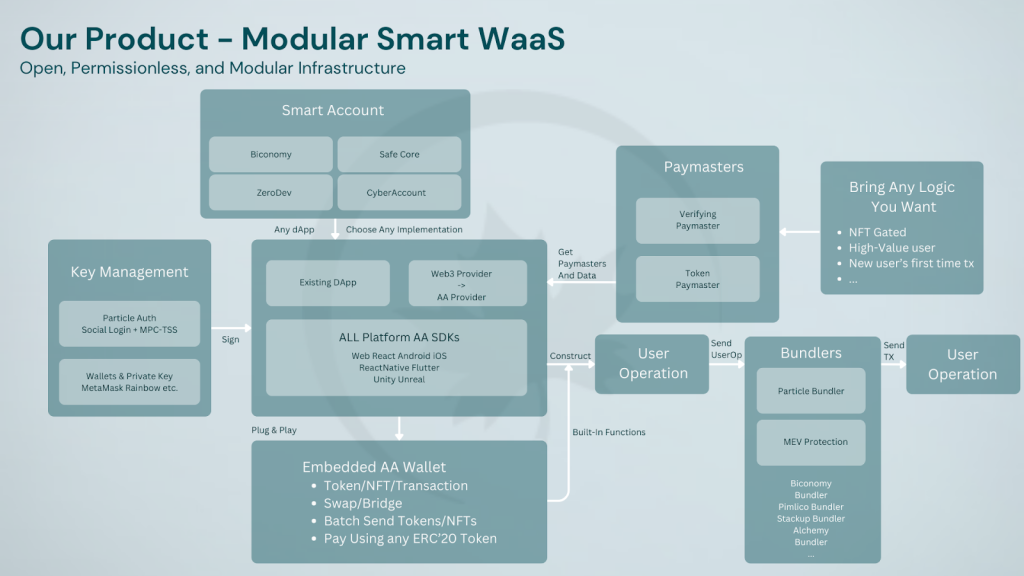
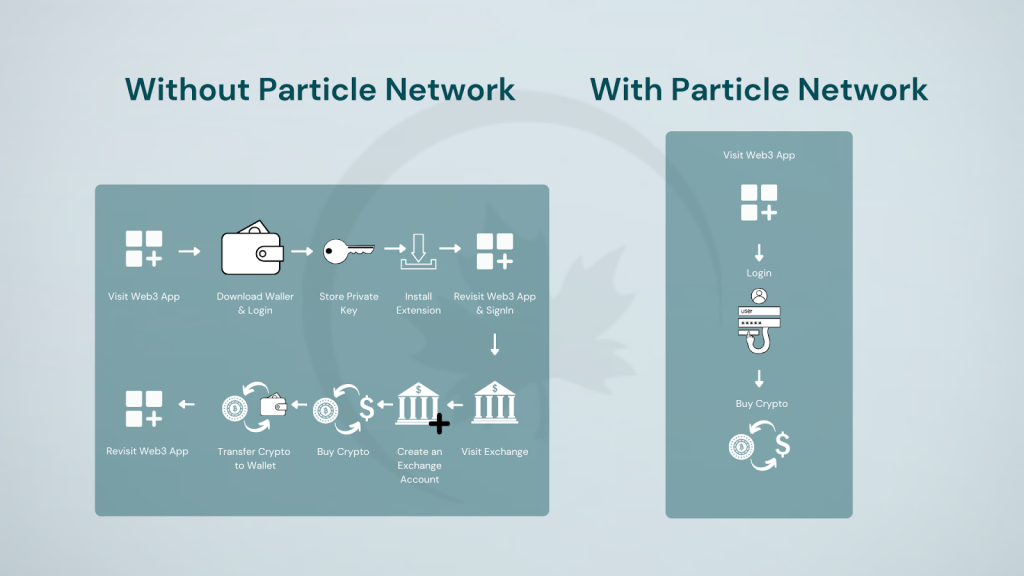
Particle Network debuted as a Wallet Abstraction service provider, enabling users to create smart contract wallets linked to their Web2 social accounts, which can then be used natively within dApp-embedded interfaces. In fact, Wallet Abstraction serves as a foundational product for Universal Accounts. Particle’s Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) stack allows developers to tap into MPC-TSS and social logins to enable self-custodial, dApp-embedded smart contract wallets. Modular Smart WaaS allows developers and users to interact natively with AA while directly tied to an MPC-secured account generated by Particle.
By modularly combining a Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) stack with account abstraction, Particle Network has produced what they call Modular Smart WaaS, one of the flagship products of their services line-up.These core functionalities address the fragmentation of users and liquidity caused by a growing number of blockchains, empowering all other chains, including Layer-1s, Layer-2s, and even Layer-3s—with enhanced interoperability. After more than 17 Million wallet activations, 10 Million UserOperations, and over 900 dApp integrations later, Particle Network is taking the next step in its evolution with its Modular L1 powering account-level chain abstraction service suite.
WaaS serves two critical functions: embedding wallets directly into platforms and enabling seamless onboarding of users through familiar authentication methods. By leveraging MPC, Particle Auth eliminates the need for complex passwords, seed phrases, browser extensions, or special hardware. Particle Network provides a 2/2 advanced TSS approach that ensures that the private key’s security is never concentrated in a single location or entity throughout its lifecycle. This method involves splitting the key into two independent shares, stored separately, ensuring that each share reveals nothing about the full key. One of these shares is stored locally by the user, and the other by Particle’s Trusted Execution Environment. All cryptographic operations are executed without combining these shares, maintaining key integrity.
Particle Network also allows the user to create a Master Password, which is used to encrypt their local key fragment, which can then be stored safely. This allows users to restore their wallets across devices with full security. A continuous key share refresh mechanism also reinforces the system’s robustness, enhancing security and making an attack virtually impossible.
Account Abstraction Features
Particle’s native compatibility with AA enables developers to adopt AA in a modular fashion, integrating it into their preferred smart account setups, Bundlers, Paymasters, and more effortlessly. Particle can also be integrated into any initial or onboarding stage within AA applications as an EOA-based Signer, even if they do not inherently utilize Particle’s AA SDK.
Historically, blockchains have utilized the externally owned accounts (EOAs) model, which are required to start transactions or execute smart contracts. However, EOAs are highly rigid and static account structures, and thus this setup limits interaction, complicates transaction batching, and requires maintaining an ETH balance for gas fees. Account abstraction (AA) eliminates the needs for EOAs, thus solving these problems by allowing smart contracts directly to initiate transactions and act as accounts for end-users. Account abstraction refers to the separation of management of an on-chain account from the end-user.
By simplifying complex processes and hiding technical intricacies behind intuitive interfaces, AA aims to make blockchain technology more accessible and user-friendly. Whether empowering developers with robust tools or providing end-users with streamlined solutions, abstraction primitives play a crucial role in bridging the gap between blockchain’s potential and its practical, widespread adoption. This empowers wallets to initiate transactions directly, meaning users can leverage programmable accounts to interact across the ecosystem, enabling functionality such as gasless transactions, automated operations,etc. In short, account abstraction uses primitives and enables the usage of smart contract wallets, enhancing user experience without exposing the underlying blockchain complexity.
Particle’s Smart Wallet taps into advanced account abstraction techniques, enabling features like social logins, recovery options, and gasless transactions, significantly lowering entry barriers for mainstream users. By abstracting complex blockchain operations and providing a streamlined, interoperable solution, Particle Network’s WaaS not only streamlines the development process but also contributes to broader Web3 adoption by making these technologies more accessible and intuitive for everyday users.
BTC Connect
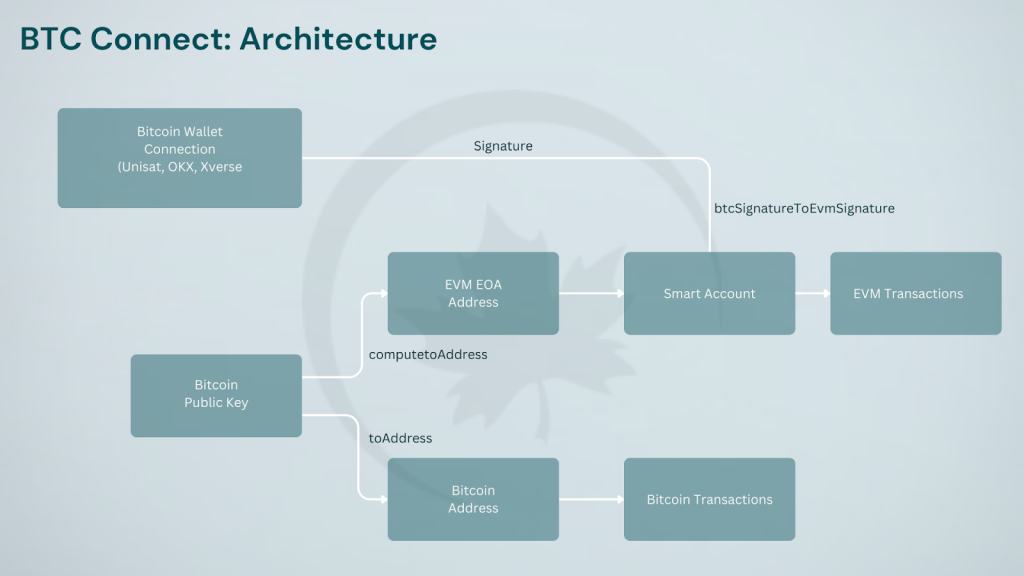
Another key product in Particle’s Wallet Abstraction suite is BTC Connect. BTC Connect is the first EVM-compatible ERC-4337 AA (Account Abstraction) protocol for Bitcoin. BTC Connect enables AA on Bitcoin by unifying users’ Bitcoin accounts and EVM-based smart accounts. This happens by assigning a Bitcoin wallet as a Signer for a smart account on a Bitcoin L2 or EVM network, making users’ existing Bitcoin wallets the sole point of interaction, without additional interactions or interfaces.
As it is designed specifically for the EVM-compatible Bitcoin ecosystem and its various dApps, BTC Connect unlocks a market that the vast majority of players in the Web3 infrastructure space are not at the forefront of. BTC Connect bridges the gap between Bitcoin and EVM-compatible chains, enabling users to interact with EVM-based dApps using their Bitcoin wallets. This solution enables BTC Layer-2s to directly serve BTC wallet users, expanding the reach and utility of Bitcoin in the broader blockchain ecosystem, including a number of potential use-cases that had previously been considered impractical from a scalability standpoint.
Interactions by the user’s Smart Account can be either funded by the account’s owner directly or pre-paid by the dApps themselves (via Paymasters). BTC Connect extends the functionality of Bitcoin wallets, allowing a user to use a single wallet to send native Bitcoin transactions, interact with the Ordinal ecosystem (Ordinals are means of creating Bitcoin NFTs by attaching data such as images, videos, and more to an individual satoshi on the base Bitcoin blockchain. Ordinal NFTs are completely Bitcoin-native. They work without changes to the Bitcoin protocol, don’t require any extra layers, and are backward compatible with the network), and execute logic (including gasless, and popup-less interactions) on compatible EVM dApps and Bitcoin L2s. It enables a number of UX-first features currently unavailable for the Bitcoin ecosystem, including – pop-upless signatures, session keys, automated transactions, simplified paths, batched transactions, and more.
With programmable accounts, users can authorize recurring transactions to be automatically executed, streamlining different on-chain services, such as subscriptions. BTC Connect is a fundamental first step for chain abstraction to encompass the Bitcoin ecosystem. Through its simple embeddings and only requiring users to authenticate transactions via their native Bitcoin wallets, it can create a seamless gateway to all kinds of use cases for the mass market, even those originally inconceivable within Bitcoin. Furthermore, As AA debuts in a nascent Bitcoin dApp ecosystem, developers building on it can incorporate it as a hugely valuable tool in their arsenal to create outstanding experiences, leading up to a future where the Bitcoin and the EVM ecosystem are seamlessly interconnected.
The Team

Particle Network was established in 2021 through a collaboration between CEO Pengyu Wang and CTO Tao Pan. Headquartered in Singapore, Particle Network’s core team houses a talented and highly committed team that believes more in the idea of “create, then tell”, rather than “create to sell”, which is a key differentiator between the kind of crypto projects that erode public faith, and the kind that build it. Pengyu Wang boasts a diverse background encompassing data analysis, management, and investment, acquired through his academic pursuits and professional engagements with various startups and tech firms. He holds a bachelor’s degree in Chemistry from Tsinghua University, completed between 2012 and 2016. Previously, he served as an Investment Manager at Softbank’s early-stage investment fund, SAIF Partners, focusing on deal origination, assessment, and execution within the consumer internet, gaming, and blockchain sectors.
Before this role, Wang worked as an analyst at China Renaissance, an investment bank specializing in financial advisory services for tech companies. Additionally, Wang is the CEO and co-founder of the highly successful social gaming platform MiniJoy in Southeast Asia. Before assuming the role of CTO and co-founder at Particle Network, Tao Pan played a pivotal role in developing the MiniJoy social gaming platform, securing a 15 Million Dollars funding from Alibaba to support the project. Pan, alongside his co-founder, attended Tsinghua University, which is a part of the C-9, a label that is dubbed as “China’s Ivy League”, making it one of China’s premier educational institutions.
Particle Network is being developed by a globally distributed team of 30+ full-time employees, and has established partnerships with the likes of Berachain, Avalanche, Arbitrum, zkSync and more. In May 2022, Particle Network achieved a significant milestone by raising 1.5 Million Dollars in a pre-seed funding round, with notable contributions from partners such as Insignia Ventures Partners, CyberConnect, BitCoke Ventures, 7 O’Clock Capital, FSC Ventures, Monad Labs, and others. Subsequently, in March 2023, the company announced a successful 7 Million Dollars seed investment round, led by ABCDE venture capital fund, with investments from entities like Animoca, Longhash Ventures, GSR Ventures, and HashKey. Furthermore, in April 2023, Particle Network secured undisclosed funding from Cobo Ventures.
On May 2, 2024, Particle Network’s incentivized L1 testnet launched, offering point rewards through the Particle Pioneer platform. In June 2024, Particle Network disclosed a substantial achievement with a 15 Million Dollars Series A funding round, spearheaded by Spartan Group and Gumi Crypto, and participation from SevenX Ventures, Morningstar Ventures, HashKey Capital, UOB Venture Management, Flow Traders, SNZ, and MH Ventures. With over 800k followers on X, formerly Twitter, Particle Network’s account is one of the most active and followed crypto project pages on X, and it is a clear pathfinder with one of it’s latest initiatives, The People’s Alliance, an effort to create a fostering ecosystem for quality crypto projects and passionate, prudent crypto participants and investors that is en route to empowering an entire host of opportunities in this industry, thereby adding a huge bag of social currency to Particle Network’s treasury of innovation.
According to the Particle Testnet V2 explorer, there have been over 7.3 Million total transactions across 1.3 Million blocks, averaging above 400k daily transactions regularly. The testnet has seen over 182 Million transactions, and there are currently over 1.49 Million users earning 27.3 Billion points in total, at an average of 18.3k points per user. Particle Network’s incentivized public testnet allows users to test out its flagship Universal Accounts and Universal Gas features to earn points for allocation of the upcoming $PARTI token. As of August 2024, Binance Labs, the venture capital and incubation arm of Binance, has also invested in Particle Network, to forward breakthroughs addressing User and Liquidity Fragmentation in Web3. Amidst the recently rejuvenated crypto VC funding macro-outlook, this investment cements a layer of validation that can welcome a cohort of prudent, committed investors for Particle Network’s further stints at exponential easing of the crypto-navigation experience.
Conclusion
Particle Network stands as a pioneer in Web3 innovation, offering a suite of solutions that tackle the core challenges hindering blockchain adoption. Its Modular Chain Abstraction Infrastructure is not just revolutionizing how users interact with multiple blockchain networks, but it has the pragmatic potential to unleash mass adoption by virtue of truly seamless usability. The platform’s strength lies in its comprehensive approach to resolving fragmentation issues. By creating Universal Accounts, Liquidity, and Gas, Particle Network has already been working on major pain-points via an approach that in itself is self-supporting and synergistic in nature. It’s recent funding galore empowers it to push further ahead, eliminating longstanding barriers to widespread blockchain use.
As blockchain technology evolves from the world of proofs and smart contracts to advanced problem-solving, tech-exponential scaling and future-proofing, Particle Network is well-positioned to become the foundation of a more accessible, more secure and a truly decentralised cryptoverse pertaining to convenient onboarding and preservation of the unique benefits of participating in the crypto-economy. Its modular design ensures adaptability to future innovations, solidifying its long-term role in the dynamic blockchain landscape.
As per it’s mission-statement, Particle Network will revolutionize how users, developers, and businesses engage with blockchain technology, making decentralized applications as user-friendly as traditional web services – a “One Account, One Balance, Any Chain” world, that could range from cross-chain DeFi protocols to privacy-focused social networks, and may even spawn new categories of frontier blockchain applications. Thus, as Web3 matures – and goes from creation to exploration to consolidation, Particle Network is positioned to drive its evolution, unifying the fragmented blockchain landscape and unlocking decentralized technologies’ true potential. It’s not just bridging Web2 and Web3 – it’s constructing the infrastructure for a more interconnected, efficient, and user-centric decentralized future.
