- Introduction
- Market Overview
- What is Shardeum?
- Product features and Competitors Comparison
- Node Architecture
- Tokenomics
- Accomplishments & Roadmap
- Team
- Conclusion
Introduction
Due to use cases like DeFi, NFTs, and Games attracting people who would not have otherwise been interested in the field, the demand for decentralized applications operating on smart contract platforms is surging. However, neither scalability nor decentralization are present in the current smart contract platforms. Lack of scalability results in sluggish transaction processing, higher transaction costs, and a poor user experience.
There are many Layer 1 solutions that have been built with the sole aim of addressing this very concern of making smart contract platforms scalable without compromising on decentralization or blockchain security.
The first layer 1 blockchain in the world to solve the scalability trilemma is called Shardeum. Low gas fees are offered permanently by Shardeum, an EVM-based, linearly scalable smart contract platform that also upholds real decentralization and reliable security. In the future, the network hopes to bring billions of daily users and a wide variety of dApps to Web 3.0.
Market Overview
The Ethereum network started a revolution in 2015 by making it possible to write smart contracts for the first time on a decentralized network. With the rising popularity of dApps on the Ethereum chain, the network’s maximum capacity of 20 transactions per second (TPS) has been surpassed. Due to this, transaction fees have increased from less than one cent in 2015 to around $50 in 2022. Due to the high transaction costs, many applications that were feasible on Ethereum are no longer viable.
As a Layer 1 scaling improvement, sharding will be used in Ethereum 2.0 to improve data availability. Sharding is the answer to the scalability trilemma, as Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin noted. Sharding offers a method to preserve security while achieving scalability and decentralization.
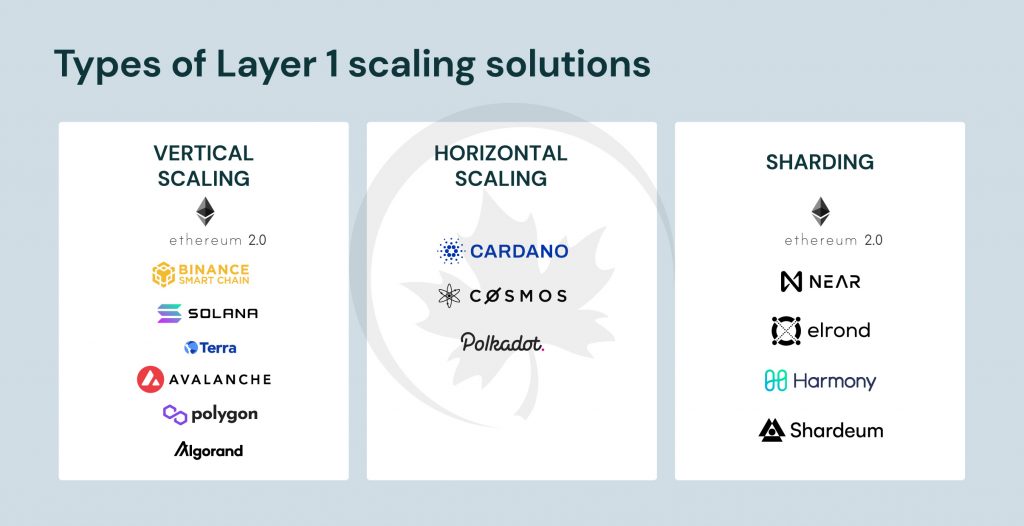
New Layer 1 solutions have been developed with a sole focus of providing higher TPS. Most of these new smart contract platforms have abandoned decentralization in order to increase TPS. In this category, some well-known smart contract systems are Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Terra, Avalanche, Polygon, and Algorand, to mention a few. They implement vertical scaling to achieve this. In vertical scaling, only if each node in the system is upgraded to include more computing, storage, and bandwidth will these platforms be able to boost TPS.
Another alternative approach to Layer 1 scaling is by using a linked system of multiple side chains or sub-chains. Platforms like Cardano, Cosmos, and Polkadot use this strategy. This strategy, known as functional sharding, enables the creation of decentralized applications that must communicate with one another on the same sidechain. Though each sidechain may be limited similarly on TPS, the total TPS combined across all side chains can be higher than what has been achieved via vertical sharding.
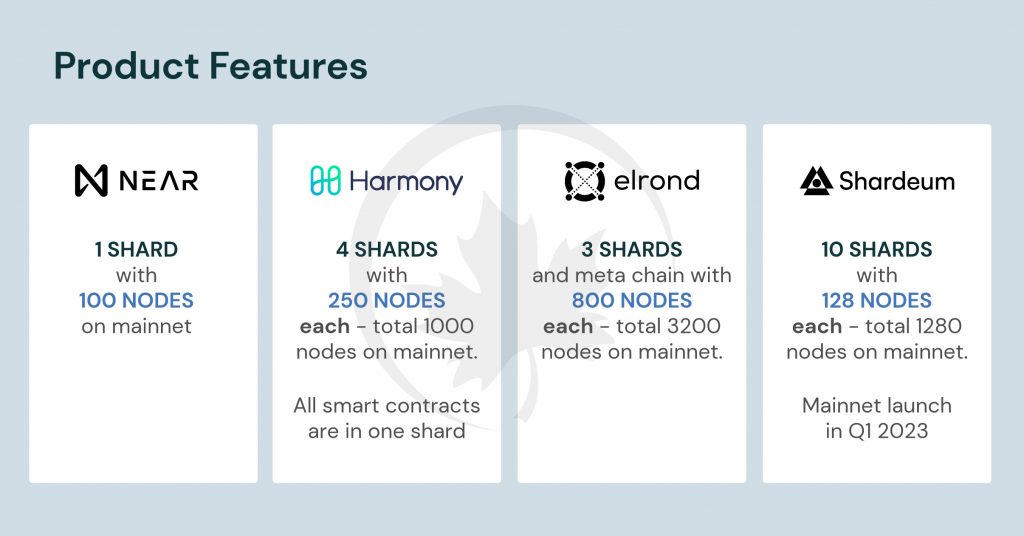
The final approach employed for Layer 1 scaling is Sharding. State sharding is done by dividing an account’s address space into a number of fixed-sized regions called shards, with each shard being assigned to a distinct network node. Platforms like Near, Elrond, and Harmony are using this strategy. Ethereum originally intended to implement state sharding, however the new method just shards the data to improve accessibility.
Sharding is still advantageous as the TPS of the entire network rises in direct proportion to the number of shards it contains. However, because the shards are static, a large number of new nodes must join the network before a new shard can be established. No actual splitting and merging of static shards has been made possible by any network up to this point. This issue is precisely what Shardeum addresses by using a cutting-edge method to get around the restrictions imposed by static shards.
What is Shardeum?
Shardeum is an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible smart contract platform offering low gas fees while being linearly infinitely scalable and maintaining true decentralization and solid security through dynamic sharding.
Sharding enables parallel processing on the network by dividing the workload on the nodes by partitioning the nodes in the network into smaller groups called shards. It also has a higher degree of decentralization as nodes being added to the network increases the throughput of the network enabling the network to scale horizontally. Shardeum aims to be the best Layer 1 smart contract platform by implementing many unique features to ensure the long term sustainability of the network while delivering the best user experience possible like linear scaling, node rotation, load detection and auto-scaling. Further, the Shardeum project aims to encourage ecosystem projects to develop cutting-edge new applications for the platform as well as port widely-liked applications that have been developed for other platforms. Incentives will be given to the ecosystem to build layer-two solutions to boost transaction throughput and decentralized bridges to enable asset transfers between Shardeum and other networks.
Hence, Shardeum aims to be a long term sustainable Layer 1 network ensuring low gas fees, high scalability, true decentralization and solid security. Thereby, overcoming the scalability trilemma coined by Vitalik Buterin.
Product features and Competitors comparison
Shardeum is an EVM compatible, smart contract platform that scales linearly using dynamic state sharding. Although it shares some similarities with state sharding platforms like Harmony, Elrond, and Near, it also has several distinctive characteristics that make it stand apart from the competition.
By evaluating & comparing 3 main platforms – Near, Elrond & Harmony that also use state sharding to solve scalability will help us understand the various unique features that Shardeum offers.
A brief introduction to these networks and their current state is shown as follows,
Shardeum’s major product features are as follows,
- EVM-based layer 1 blockchain
Total backward compatibility for any dApp that runs on Ethereum Virtual Machine will run on Shardeum as well. And, shorter learning curve for developers as Solidity and Vyper are the smart contract language for Shardeum development.
- Linear scalability & low gas fees forever
In order to achieve linear scaling and guarantee cheap transaction fees even as usage increases, any node that joins the Shardeum network immediately boosts the network’s capacity overall and transactions per second (TPS). Shardeum retains atomic composability which is extremely complex to achieve. It also achieves faster transaction processing as the consensus is done at transaction level and not block level.
- Anyone can operate a node
Offloading past data to archive nodes and increasing the number of nodes helps keep hardware requirements for validator nodes in the permissionless Shardeum network low.
- Immediate finality & low latency
To ensure minimal latency, all transactions are promised to be executed quickly. They are also promised to be irreversible after processing, resulting in immediate finality. - Solid security
The security of the network is increased by a leaderless Proof-of-Quorum (PoQ) consensus method, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with slashing, standby nodes, node rotation, and permissionless participation. - High fairness & high efficiency
To maintain fairness and eliminate miner extractable value, Shardeum processes transactions on a first-come, first-served basis with the same gas rate for all transactions. Shardeum is an eco-friendly and sustainable PoS network. Further, Shardeum uses archive nodes to offload historical transaction data from validator nodes. This means lesser data storage, lesser hardware requirements, lesser time to join the network for a validator – thereby increasing decentralization.
Major features offered by Shardeum and how these compare with Near, Elrond & Harmony is described below,
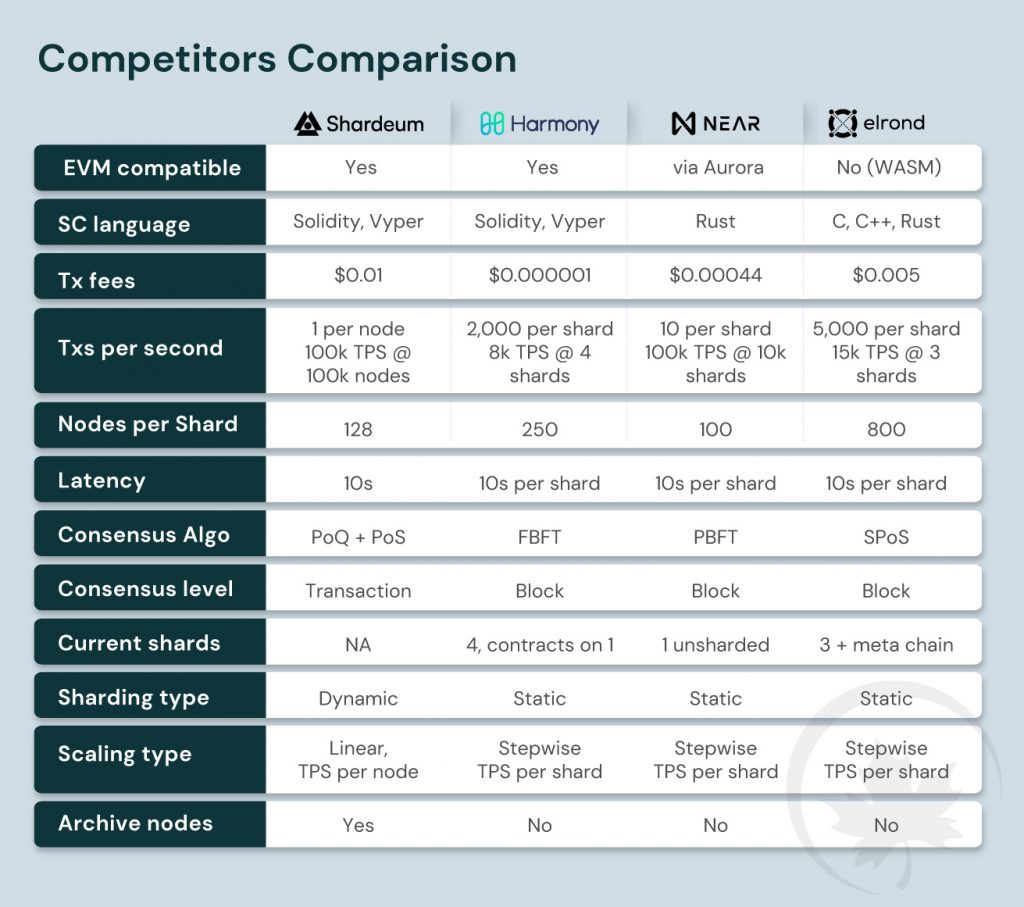
The above comparison illustrates that Shardeum offers a variety of distinctive characteristics that are not present in other networks. The usage of archive nodes to transfer historical transaction data from validator nodes is a significant Shardeum-specific feature. This implies that the validator nodes just need to store the state data and can join the network much more quickly. This enhances the degree of decentralization, lowers the hardware requirements for running validators, and makes validators available to more common users while maintaining solid security of the network.
Node Architecture
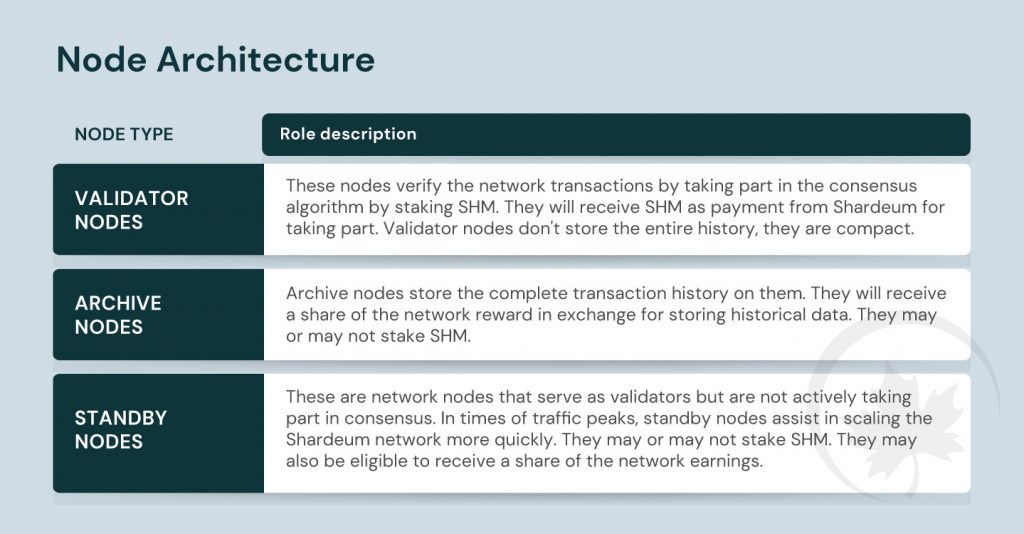
A unique consensus algorithm that combines Proof-of-Quorum (PoQ) and Proof-of-Stake completes Shardeum’s innovative technology (PoS). The network will be more secure because of the consensus algorithms’ trustless voting and stake by validator nodes. Instead of using block-level consensus, the network uses transaction-level consensus where each transaction is handled in the order in which it is received. This enables a transaction to be processed concurrently across shards as opposed to sequentially as with block-level consensus.
The different types of nodes of the Shardeum network and a brief description of their varied functions are as follows,
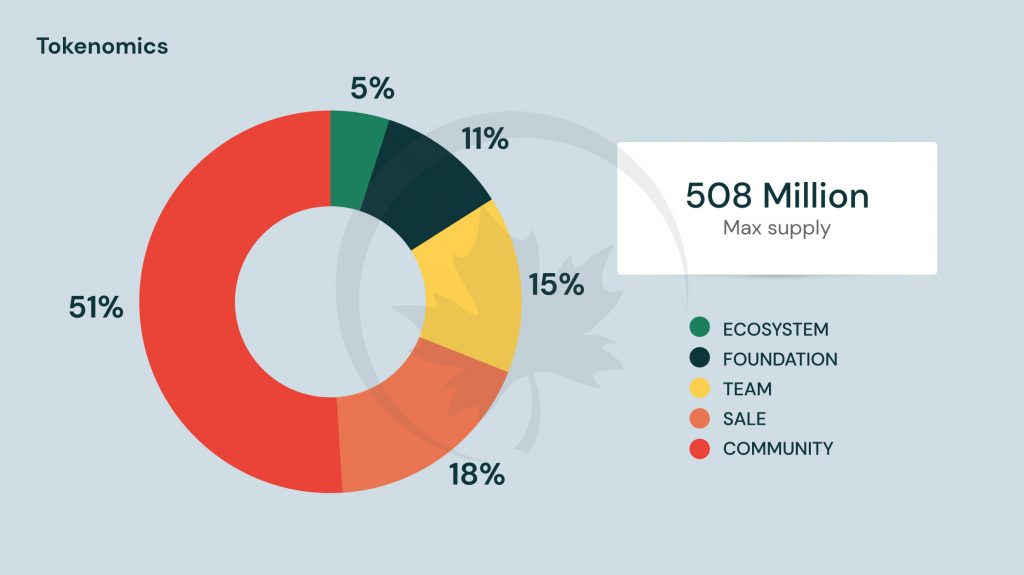
Tokenomics
SHM is the native Shard coin of the Shardeum network.
Token Utility
The token will serve as payment for supplying resources to the network, validator, archive, and standby nodes will mine the coin. The token will be employed to cover the gas costs incurred by the Shardeum network when executing transfer operations and smart contracts.
Accomplishments & Roadmap
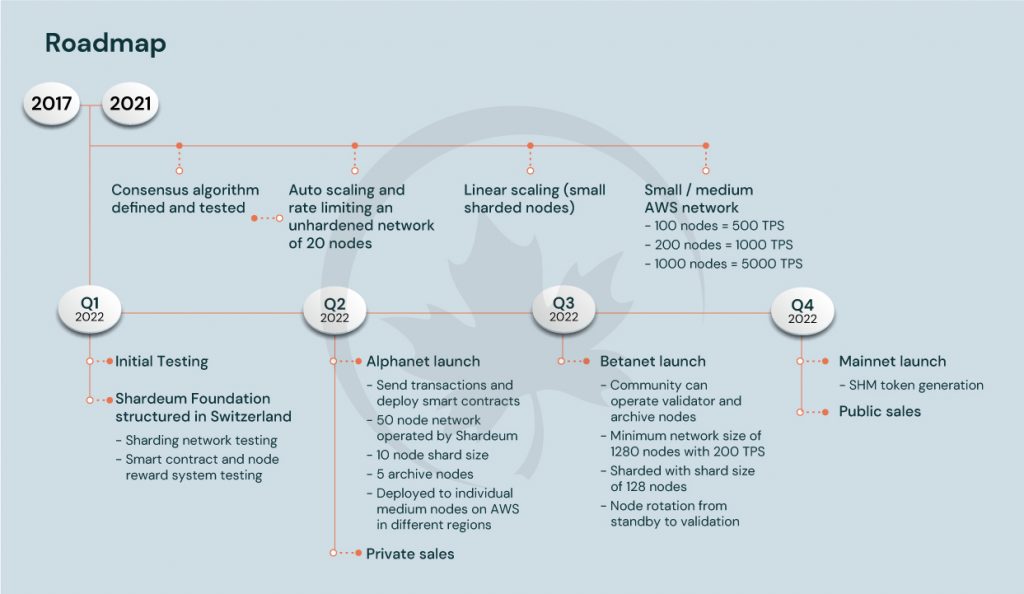
Shardeum was started in early 2022 and is still under development. However, the Shardus technology employed at the protocol level has been in development since 2017. A system for building distributed ledgers that can scale linearly is called Shardus. Shardus technology is the core behind the Shardeum smart contract platform.
A network of 1000 nodes running on AWS t3.medium hardware was demonstrated to be able to process 5000 TPS of signed coin transfer transactions across shards during the Q3 2021 upgrade event. With 1000 total nodes and a shard size of 20 nodes, the network had 50 dynamic shards. In an earlier event, the network detected the transaction load and grew automatically by enabling more standby nodes to turn into active nodes when the TPS climbed. This illustrates auto-scaling in action. The network afterwards shrank back down by deleting some of the active nodes after the load was lifted.
Shardeum launched Alphanet (Liberty) 1.0 on April 26, 2022 with 15 transactions per second (TPS). On the latest version of our testnet, Liberty 2.0, with complete sharding capabilities 100 TPS using ERC20 token transfers was achieved. Shardeum has been able to achieve this in less than 4 months since launch of Liberty 1.0. Also, there are 100K+ users on the testnet network.
The following examples will help understand the TPS scale of various platforms.
Shardeum is on track with their development efforts and will launch on mainnet soon by utilizing the Shardus architecture and integrating EVM and smart contracting functionalities at the application layer.
Roadmap is as follows,
Team
The founding members of Shardeum are Nischal Shetty and Omar Syed. Shardeum team is spread across US, India & Myanmar.
Nischal Shetty: Co-founder. The largest cryptocurrency exchange in India, WazirX, which has over 10 million members, was founded and is led by Nischal Shetty. Nischal is a well-known businessman who has spent more than ten years developing and marketing international products from India. Nischal, a software engineer by training, founded Crowdfire, a social media management website that has over 20 million users. Nischal is also included in Forbes’ list of the “30 under 30”. Nischal, a fervent proponent of blockchain technology, has been involved in the Indian cryptocurrency community since its start. With his Twitter campaign #IndiaWantsCrypto, Nischal has been lobbying for favorable crypto regulation in India for more than 1000 days. His goal has been to make cryptocurrency available to every Indian.
Omer Syed: Co-founder. He organized the Shardus project from 2017 to build a linearly scalable blockchain. Omar has spent the last three decades working with huge companies like NASA, Yahoo, and Zynga to create scalable, fault-tolerant distributed systems. Omar graduated with both a B.S. and an M.S. in Artificial Intelligence from Case Western Reserve University. Omar was associated with a number of start-ups, including the first stock sentiment research website and the first matrimonial website. The strategy board game Arimaa was created by Omar and his son Aamir. Omar also presented the Arimaa Challenge Prize to encourage ground-breaking AI research. Omar’s long-term goal is to see a society without hunger or poverty where everyone receives an unconditional basic income based on a reliable cryptocurrency.
Conclusion
The demand for decentralized applications has been growing exponentially as more people are understanding the superior benefits possible with the underlying blockchain technology.
Multiple use cases like DeFi, NFTs, Gaming, P2P transfers are demanding high TPS with no compromise on decentralization and security enforced by blockchain.
Shardeum is the first linearly scalable smart contract platform that increases TPS linearly by adding more nodes to the network. It is also EVM based and provides low gas fees forever while maintaining true decentralization and solid security enabled through dynamic sharding.
Some additional metrics to understand the scale of Shardeum are as follows,
- $0.01 estimated transaction cost
- Minimum of 1280 validators
- 10k+ community members
- 100k+ estimated transactions per second (TPS)
Shardeum solves the scalability trilemma, first quoted by Vitalik Buterin. And, aims to become a leading Layer 1 solution in the long term. The team is very strong and focused in making this happen. They have been involved in creating a sharding based linearly scalable blockchain since 2017.
Shardeum is ideally placed to make Layer 1 scaling with high TPS and low gas fees a new normal for the masses, and we are happy to contribute to their mission.
